● Static 메소드
static 멤버변수와 같이 프로그램 구동전에 메모리에 로딩되어 객체 생성없이 사용할수 있는 메서드
main 메소드에서 사용시에 메서드 이름앞에 클래스의 이름을 붙여서 사용합니다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class StaticC{
public static void print() {
System.out.println("static 메스드로 출력하였습니다");
}
public static void prn() {
print();
}
}
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StaticC.print(); // 객체 생성없이 멤버메서드(static)를 호출합니다
|
cs |
- static 메서드 호출시에 따로 객체 생성 없이 (클래스명).(static 메서드명) 으로 바로 호출해서 사용
- 이전에 같은 클래스 내에서 생성한 메서드는 그냥 '메서드명();'으로 호출했었음
● java.lang : import 하지 않아도 원래 import되어져서 사용할수 있게 존재하는 패키지(클래스)
간단한 공용기능을 제공하기 위한 Math 클래스 (java.lang 패키지안에 있는 클래스)
Math 클래스 안에 public static int abs(int n){ } 와 같은 양식의 sqrt, random 메서드 가 있습니다
-abs : 절대값 계산 메서드,
-sqrt : 제곱근 계산 메서드,
-random : 난수 발생 매서드
※Math 클래스
1)random();
Math 클래스의 random 메서드는 Random 클래스의 nextInt() 메서드와 양식은 다르지만 역할을 같은 메서드입니다
다만 Math 클래스의 random 메서드는 static 메서드 이므로 Math.random();와 같이 사용하고
Random 클래스의 nextInt() 메서드는 동적멤버메서드 이므로 import도 별도로 해야하고
new 명령으로 객체 생성후 호출객체를 앞에 두고 사용합니다
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1부터 45까지의 정수 출력
Random rd = new Random();
int r = rd.nextInt();
System.out.println( r % 45 + 1 );
//0부터 44까지의 정수 출력
double d = Math.random();
System.out.println( (int)(d * 45) );
|
cs |
- Math 내의 메소드는 따로 import할 필요도 없고, 따로 객체 선언도 필요가 없다.
2)abs();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = -10;
System.out.printf("num = %d, num 변수의 절대값 = %d\n",num, Math.abs(num));
|
cs |
-Math.abs(num) 으로 바로 사용
3)sqrt();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
num = 9;
System.out.printf("num 변수의 제곱근 = %.2f\n", Math.sqrt(num));
|
cs |
-Math.sqrt(num) 으로 바로 사용
※ Integer 클래스 (int 타입과 매핑되는 클래스)
- Integer 클래스의 parseInt 메소드는 문자열로 되어있는 정수값을 int 타입으로 변환
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strNum1 = "123";
String strNum2 = "456";
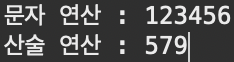
System.out.println("문자 연산 : " + (strNum1 + strNum2) );
System.out.println("산술 연산 : " + (Integer.parseInt(strNum1) + Integer.parseInt(strNum2)) );
|
cs |
※String 클래스 (int 또는 double 형 자료를 String 으로 변환 - valueOf() )
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intNum1 = 456;
int intNum2 = 789;
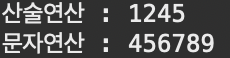
System.out.println("산술연산 : " + (intNum1 + intNum2));
System.out.println("문자연산 : " + (String.valueOf(intNum1) + String.valueOf(intNum2)) );
|
cs |
※ Double 클래스 (double 타입과 매핑되는 클래스)
-Double 클래스의 parseDouble 메소드는 문자열로 되어있는 실수값을 double 타입으로 변환
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Class22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strNum1 = "10.75";
String strNum2 = "5.2";
// 문자열 결합
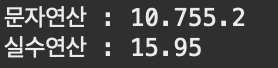
System.out.println("문자연산 : "+(strNum1 + strNum2) );
// 문자열의 값을 실수로 변환한 후 연산
System.out.println("실수연산 : "+(Double.parseDouble(strNum1)+ Double.parseDouble(strNum2)));
|
cs |
'JAVA > 수업 복습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바 공부기록 41 - Private으로 지정된 Static 변수 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
|---|---|
| 자바 공부기록 40 - 인스턴스 메서드 / 스태틱 메서드 / 인스턴스 변수 / 스태틱 변수 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| 자바 공부기록 38 - Static의 정의 / Static 변수 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| 자바 공부기록 37 - 생성자 메소드(매개변수) / 멤버메소드 오버로딩/ this (0) | 2022.04.27 |
| 자바 공부기록 36 - 생성자(Constructor) (0) | 2022.04.26 |